Adding a Prefix to the Auto Numbering
- In the system, you can adjust the serial numbering for all operations and inputs in the account.
- From the main menu, click on “Settings“.
- Choose “Auto Number Settings” from the menu.
- Click on one of the input elements from the list on the left to adjust its serial.
- Adjust the sequence method:
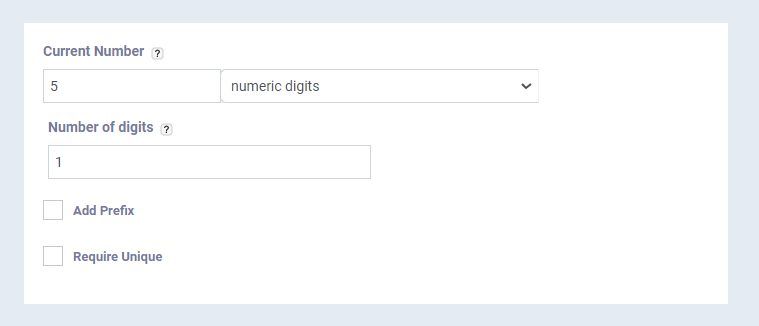
- Current Number: Shows the current serial number for the selected input type. You can set the format of the series and choose from: (numeric digits- lowercase letters – uppercase letters – lowercase letters followed by numeric digits – uppercase letters followed by numeric digits).
- Number of digits: Specify the number of digits that the series consists of: for example, 3 digits (001), or 4 digits (0001).
- Click on the checkbox “Require Unique” to ensure that the serial number is not repeated for the same entry more than once.
- Click on the checkbox “Add Prefix” to set a fixed or variable encoding that starts before the serial number.
Steps to assign the Prefix to the Serial Numbering
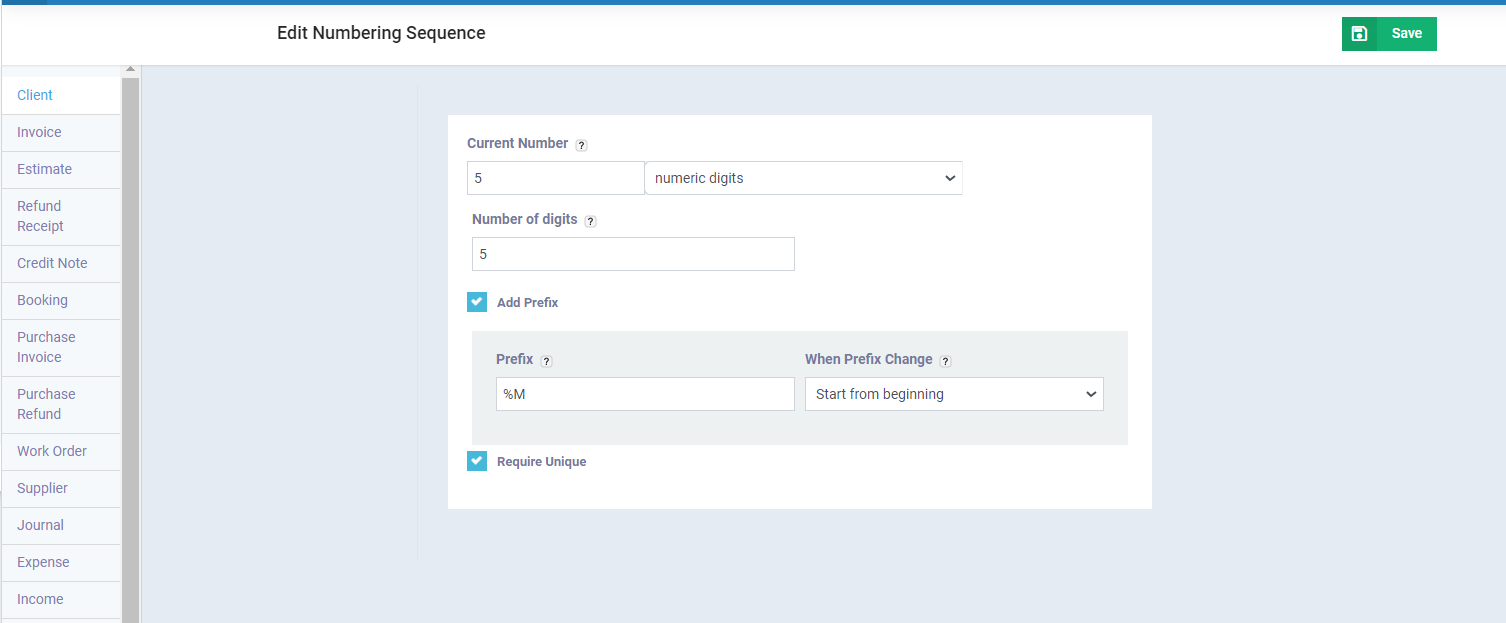
When you click on “Add Prefix”, the following fields appear, which require you to assign a value to them for the prefix to be set correctly:
Prefix: In this field, you can assign either a fixed value or a variable value that changes with each invoice.
When Prefix Change: In this field, you choose the type of action required when the existing prefix is modified or changed.
How to Add a Variable Prefix
To be able to add a variable prefix, you can use one of the following variables in the “Prefix” field:
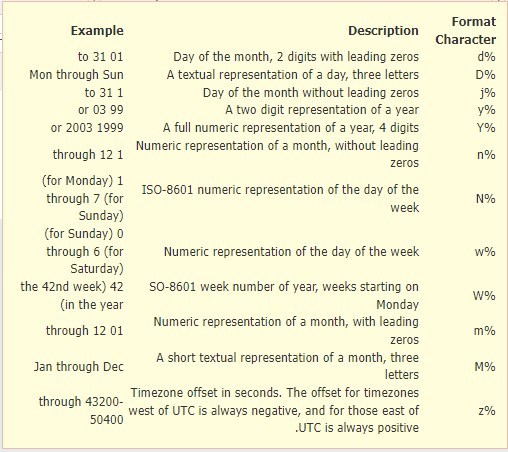
- d%: This variable represents the “day” number on which the transaction was recorded and consists of two digits starting with “0”, for example, “from 01 to 31”.
- D%: This variable represents the “day” name on which the transaction was recorded, written with only three letters, for example, “Sun, Mon…”.
- j%: This variable represents the “day” number on which the transaction was recorded and consists of only one digit without a leading “0”, for example, “from 1 to 31”.
- y%: This variable represents the “year” number in which the transaction was recorded and consists of only two digits, for example, “23” which refers to the year 2023.
- Y%: This variable represents the “year” number in which the transaction was recorded and consists of 4 digits, for example, “2023”.
- n%: This variable represents the “month” number in which the transaction was recorded, for example, “from 1 to 12”.
- N%: This variable represents the numerical order of the days of the week, for example, “from 1 to 7 representing Monday to Sunday”.
- w%: This variable represents the numerical order of the days of the week, for example, “from 0 to 6 representing Sunday to Saturday”.
- W%: This variable represents the current week number of the year (week starts from Monday), for example, “190001” which represents week 19 plus the invoice number 00001.
- m%: This variable represents the “month” number in which the transaction was recorded and consists of two digits (starting with “0”), for example, “from 01 to 12”.
- M%: This variable represents the “month” name in which the transaction was recorded, written with only three letters, for example, “Jan, Feb, Mar…”.
- z%: This variable represents the time zone offset in seconds. Regions west of the Coordinated Universal Time are always negative, whereas those to the east are always positive, for example, “between 43200 – 50400“.