Income Statement – Balance Sheet – Cash Flow Statement on Daftra and How to Read Them
To prepare and read financial statements on Daftra, it is essential to understand the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement. Financial statements are important for several reasons. They provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health, and by analyzing these statements, businesses can identify trends, assess profitability, manage resources efficiently, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Income Statement
An Income Statement is a financial document that summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period.
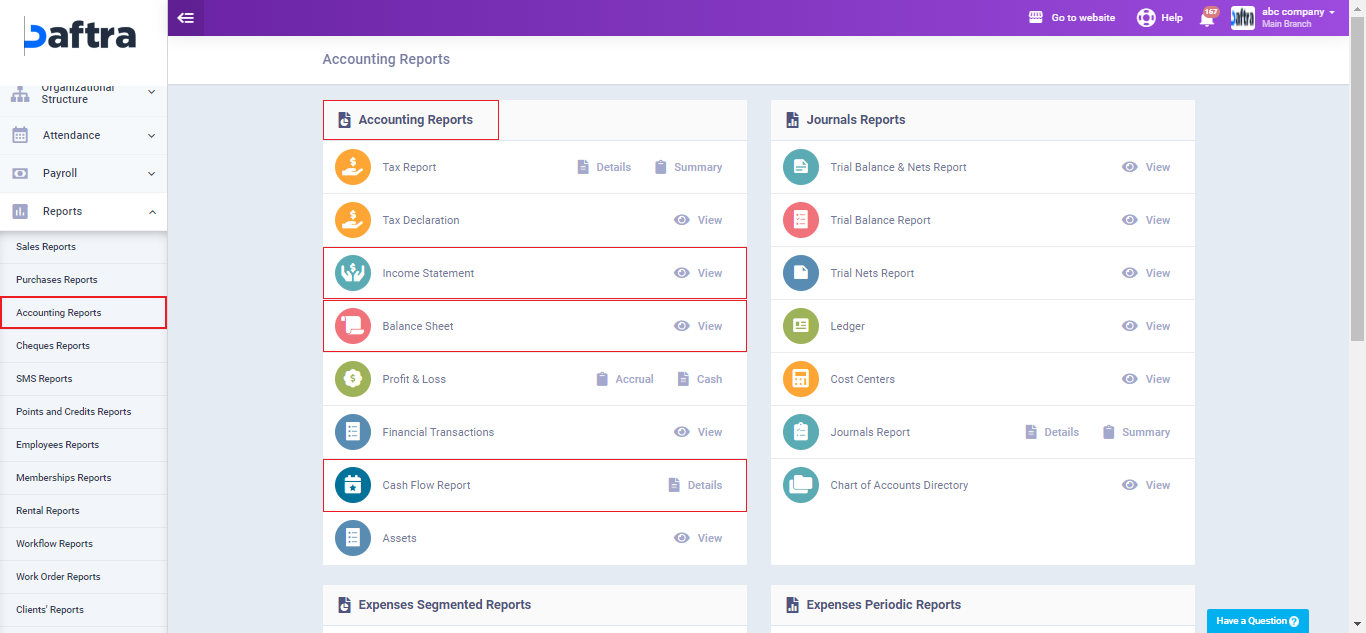
To view an income statement report in Daftra follow the steps below:
From the main menu click on “Reports“, choose “Accounting Reports“, then click on “Income Statement“.
The “Income Statement” report will appear on a new page. You can apply a number of additional filters to the report, including: Date Range, Accounts Branch, Journal Branch, Cost Centers, and others.
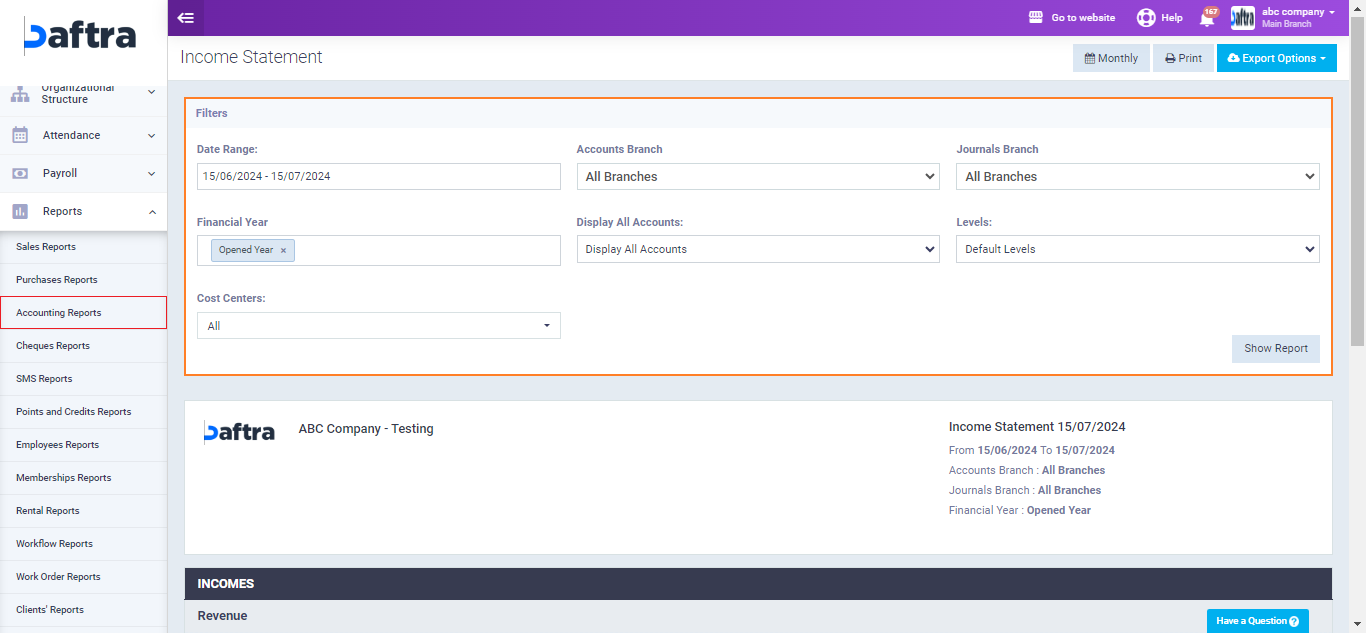
After applying the required filters click on “Show Report“, then a detailed income statement will be generated as displayed in the image below.
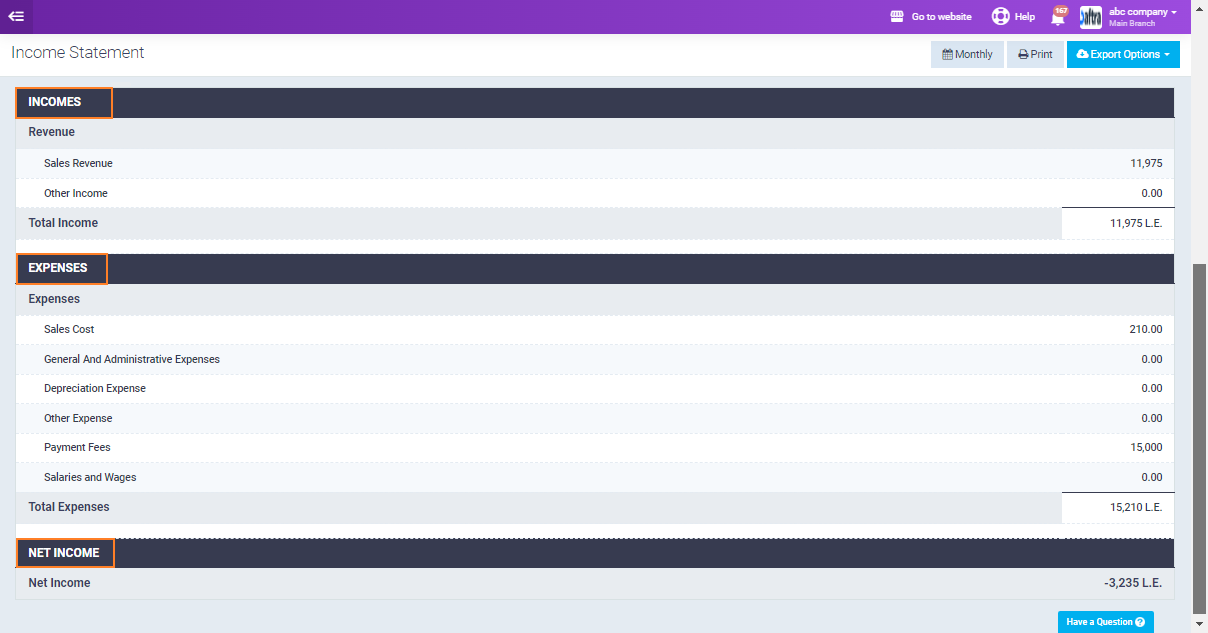
The first part included in the statement is the “Incomes” and it includes the following:
Revenue: The total amount of money earned from the sale of products or services and other sources.
You’ll find them listed in the form of 3 fields:
- Sales Income: Income generated from the core business activities, primarily the sale of goods or services.
- Other Income: This includes all other sources of revenue that are not part of the company’s core business operations.
- Total Income: The sum of Sales Income and Other Income. It represents the overall revenue generated by the company during a specific period.
The next part of the statement is:
Expenses: These are the costs incurred by the company to generate revenue and maintain operations. Understanding expenses is crucial for assessing the company’s profitability and efficiency.
You’ll find them listed in the form of several accounts:
- Sales Cost: Direct expenses associated with producing products or services sold by the company.
- General and Administrative Expenses: Costs necessary for overall business operations, including office supplies, utilities, rent, and administrative salaries.
- Depreciation Expense: Allocation of asset costs over their useful lives to reflect wear and tear.
- Payment Fees: Costs incurred from processing payments, such as credit card processing fees.
- Salaries and Wages: Employees’ salaries, wages, bonuses, and benefits.
And the final part of the statement is:
Net Income (Net Profit or Earnings): The final profit after all expenses, including taxes, have been deducted from total revenue. This is the “bottom line” of the Income Statement.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
To view the Balance Sheet in Daftra follow the steps below:
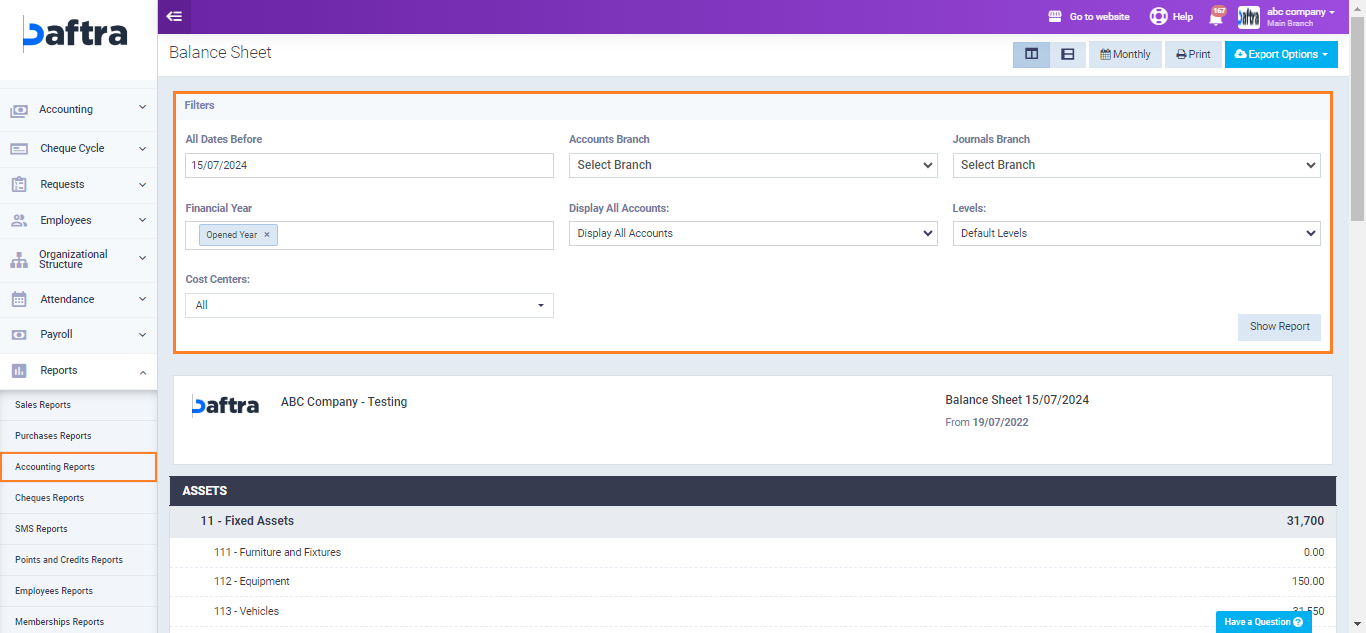
Click on “Accounting Reports” from the dropdown menu of “Reports” in the main menu, then choose “Balance Sheet“.
Set your desired filters from the filters section, then click on “Show Report“.
Then the balance sheet will be displayed in the form of three main sections:
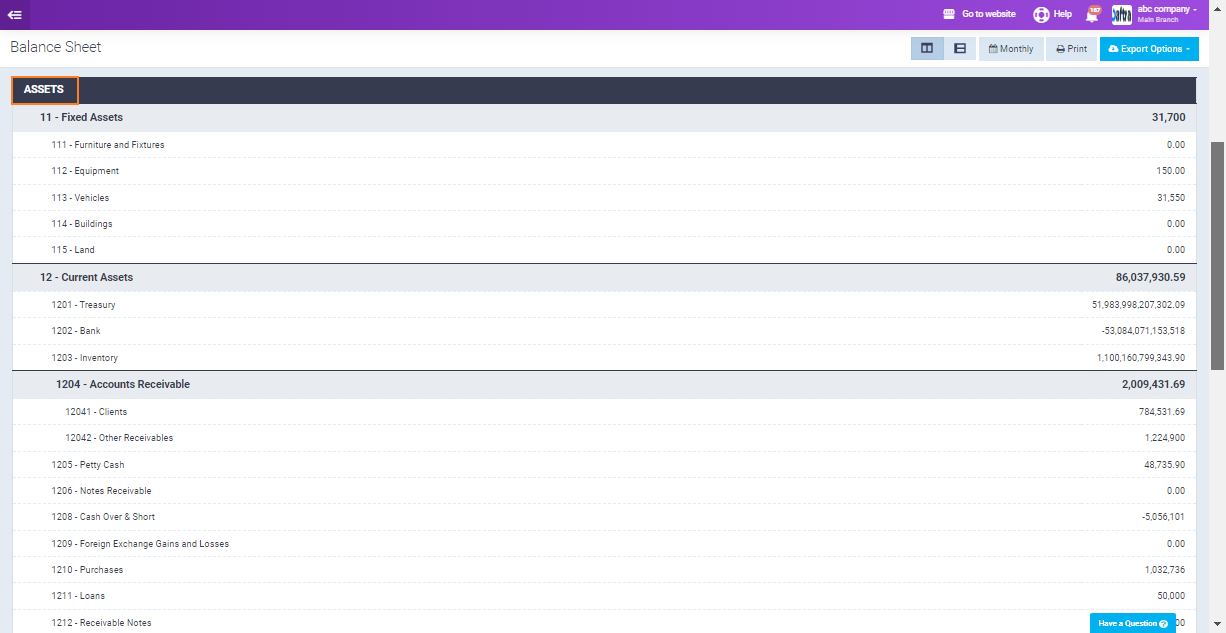
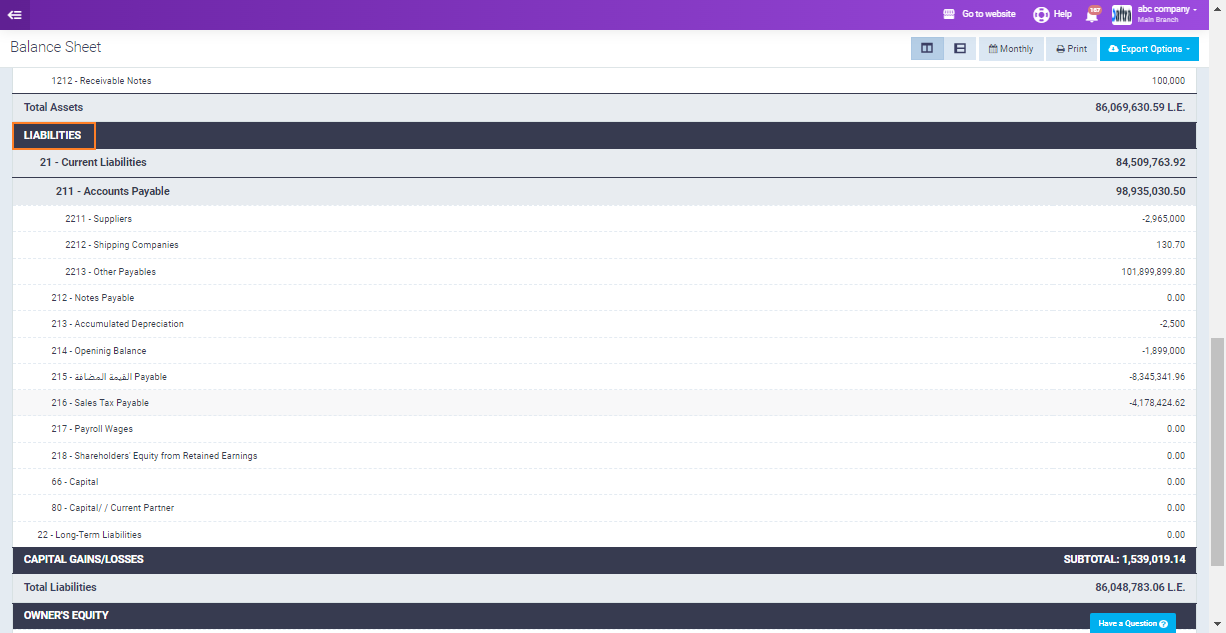
Assets: These are resources owned by the company, which can include:
- Fixed Assets: Long-term resources like furniture, equipment, and vehicles.
- Current Assets: Short-term resources like Treasuries, Banks, and Inventory.
- Account Receivable: Money owed to the company by customers.
Liabilities: These are obligations or debts owed by the company to external parties. There are two types of liabilities:
- Current Liabilities: Short-term debts payable within one year, such as Accounts Payables.
- Long Term Liabilities: Debts payable over a longer period, such as Long-term Loans.
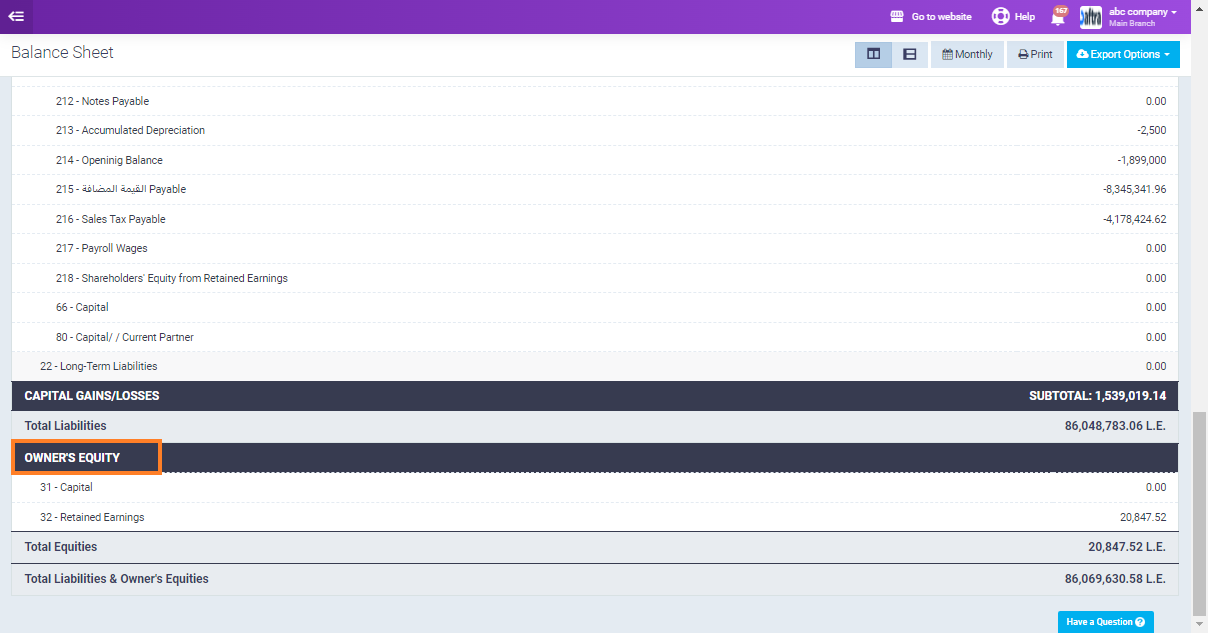
Owner’s Equity: This represents the net worth of the company and is calculated as assets minus liabilities. It includes items such as retained earnings and capital.
Understanding the Structure:
The balance sheet follows the equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
Assets are listed in order of liquidity (how quickly they can be converted into cash).
Liabilities are typically listed in order of when they are due for payment.
Owner’s Equity clarifies how much of the company is owned by shareholders versus retained earnings.
Cash Flow Report
From the “Accounting Reports” choose the “Cash Flow Report“. Set the required date range and branch then click “Show Report“.
A cash flow report, or cash flow statement, is a financial document that provides a summary of the cash inflows and outflows of a company over a specific period.
A cash flow report is typically divided into three main sections:
- Cash Flow From Operations: Cash inflows include cash received from customers, interest, and dividends, while cash outflows encompass cash paid for expenses, salaries, rent, taxes, and other operating expenses.
- Cash Flow From Investments: This section includes cash outflows for purchasing assets, investments, or businesses, and cash inflows from the sale of these assets, investments, or businesses.
- Cash Flow From Finance: Cash inflows from issuing stock or loans, and cash outflows for repaying loans, paying dividends, or repurchasing stock.